Schedule a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Composition and Properties
Aqueous Solutions
Aqueous solutions are a fundamental concept in chemistry and are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and water treatment. In this response, we will delve into the composition and properties of aqueous solutions, with a focus on their characteristics, applications, and importance.
Composition of Aqueous Solutions:
- Aqueous solutions are mixtures of two or more substances in which one substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent), which is typically water.
- The solute can be a solid, liquid, or gas, and it is usually present in small amounts compared to the solvent.
- The solvent, in this case, water, makes up the majority of the solution and provides the necessary environment for the solute to dissolve.
Properties of Aqueous Solutions:
Aqueous solutions exhibit several distinct properties that are influenced by the composition of the solution. Some of these properties include:
- Viscosity: The viscosity of an aqueous solution depends on the concentration of the solute and the size of its particles.
- Density: Aqueous solutions can have a density that is greater, less than, or equal to that of water, depending on the solubility of the solute.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of an aqueous solution is elevated by the presence of non-volatile solutes, such as salts and sugars.
- Melting Point: Some solutes can lower the melting point of water, creating a phenomenon known as freezing-point depression.
Temper Filler Applications:
Aqueous solutions are used in various applications, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Many medications are formulated as aqueous solutions to improve their solubility and bioavailability.
- Food Processing: Aqueous solutions are used to prepare foods such as sauces, soups, and beverages.
- Water Treatment: Aqueous solutions are used to remove impurities from water and other liquids.
Importance of Aqueous Solutions:
Aqueous solutions play a crucial role in many industries and our daily lives. Their unique properties make them suitable for various applications, and their versatility has led to the development of numerous products and technologies.
In conclusion, aqueous solutions are complex mixtures of substances that exhibit distinct properties influenced by their composition. From pharmaceuticals to food processing, water treatment, and beyond, aqueous solutions have a significant impact on our daily lives and industries. Understanding their composition and properties is essential for developing effective products and technologies.
Typical concentrations range from 5% to 20%
This composition typically consists of a mixture of polymers, resins, and fillers.
The polymers provide the strength and adhesion properties to the filler material.
The resins act as the binder, holding the polymers and fillers together in the desired shape.
Fillers, on the other hand, contribute bulk volume and cost-effectiveness to the final product.
Common types of fillers used in this composition include:
- Silica
- Fumed silica
- Borates
- Pigments (e.g. titanium dioxide, iron oxide)
The proportions of each component can vary depending on the specific application and desired properties of the final product.
Typical concentrations range from 5% to 20% in weight, with 10% being a common target for many applications.
The choice of filler material depends on factors such as:
- Desired physical properties (e.g. strength, thermal stability)
- Cost and availability
- Chemical resistance and compatibility with other components
A higher proportion of fillers can lead to improved:
- Bulk volume and cost-effectiveness
- Thermal stability and durability
- Mechanical strength and stiffness
However, excessive filler content can result in reduced:
- Adhesion and cohesion between components
- Chemical resistance to solvents and chemicals
- Optical clarity and transparency
The choice of polymer matrix and resin binder also plays a crucial role in determining the overall properties of the final product.
pH levels between 4 and 7
The composition of solutions within this specific pH range is crucial in understanding how they will interact with temple fillers.
Solutions with a pH level between 4 and 7 are considered acidic to neutral, depending on their exact concentration.
For instance, a solution with a pH of 4 is slightly acidic, whereas one with a pH of 7 is neutral.
A pH level of 5.6 falls into the mildly acidic category, while 6.0 and above are considered neutral or weakly alkaline.
The presence of substances such as baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) in temple fillers can affect their pH levels when mixed with other solutions, thereby influencing their interactions.
This is why it’s essential for dental professionals to carefully consider the pH levels of various solutions and how they might interact with different materials within temple fillers.
Understanding these properties allows professionals to predict potential outcomes when using these solutions in clinical settings, ensuring patient safety and effective treatment.
A key factor influencing the interaction between temple filler composition and pH is the hydroxylapatite content of the filler material itself.
The incorporation of substances like glycerin can also impact a solution’s pH level, as it acts as a humectant that helps retain moisture in the oral environment.
This can be particularly relevant when using solutions with high glycerin concentrations, as these may exhibit more extreme pH levels.
Additionally, factors such as temperature and atmospheric conditions also play a role in shaping the pH of temple filler solutions over time.
For instance, changes in humidity or exposure to air can cause pH shifts due to the reaction with atmospheric moisture.
As a result, professionals must carefully monitor pH levels when using temple fillers, especially during prolonged use or in environments with variable temperature and humidity conditions.
Viscosity decreases with increasing concentration
The concept of composition and properties is crucial in understanding how ingredients interact with each other in a mixture, such as a temple filler.
In the context of temple fillers, which are used to coat or fill glass containers with a uniform layer of material, the composition and properties of the filler play a significant role in determining its performance.
A key property of temple fillers is their viscosity, which is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity affects how easily the filler can be applied to the container and how evenly it will coat the surface.
Viscosity decreases with increasing concentration, meaning that as the filler becomes thicker and more concentrated, its resistance to flow decreases.
This phenomenon is known as dilational rheology, where the viscosity of a fluid changes in response to changes in pressure or temperature.
In temple fillers, this means that as the concentration of the filler increases, it will become easier to apply and coat the container more evenly.
However, if the concentration becomes too high, the filler may lose its flow characteristics, leading to uneven coating and potential defects in the final product.
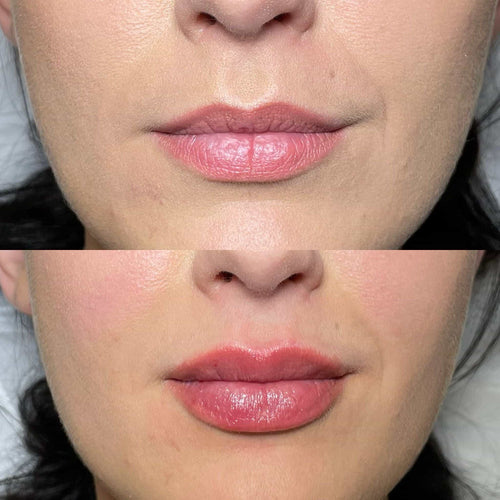
The optimal viscosity of a temple filler is typically achieved at a specific concentration, which is often referred to as the “optimum filler level” or “OFL.”
At this point, the filler has a balance of flow characteristics, surface tension, and wetting properties that enable it to coat the container evenly while maintaining its structural integrity.
The composition and properties of temple fillers can be adjusted by varying factors such as the type and proportion of ingredients used, temperature, and shear rate during application.
Understanding the relationship between viscosity, concentration, and flow characteristics is crucial for formulators to produce high-quality temple fillers with optimal performance and uniformity.
Furthermore, knowing the properties of a filler can help identify potential issues during the production process, such as clogging, drying out, or uneven coating, which can affect the final product’s quality and appearance.
Thermal Stability
The composition of a temple filler is typically a mixture of various components, including pigments, binders, and fillers.
Pigments are the coloring agents that provide the desired color and appearance to the temple filler.
Binders, on the other hand, are the materials that hold the pigments and fillers together, providing cohesion and adhesion to the mixture.
Fillers, which make up the majority of the composition, serve to reduce the cost of production while maintaining the desired properties of the temple filler.
The type and proportion of each component can significantly affect the final properties of the temple filler.
Thermal stability refers to the ability of a material to withstand changes in temperature without undergoing significant degradation or alteration.
In the context of temple fillers, thermal stability is critical, as these products are often exposed to varying temperatures during use and storage.
Materials with high thermal stability can resist thermal shocks, retain their color and consistency over a wide range of temperatures, and maintain their performance in demanding environments.
The specific requirements for thermal stability will depend on the intended application and use of the temple filler.
For example, temple fillers used in outdoor applications may require higher thermal stability to withstand exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations.
In contrast, indoor temple fillers may not require the same level of thermal stability, as they are typically shielded from extreme temperature extremes.
The properties of a temple filler that contribute to its thermal stability include its melting point, glass transition temperature, and thermal diffusivity.
A material with a high melting point can resist thermal degradation and maintain its structure and properties over a wide range of temperatures.
A material with a low glass transition temperature (Tg) will typically exhibit more pronounced changes in its physical properties as it approaches Tg, making it less suitable for applications requiring high thermal stability.
Thermal diffusivity is another critical property that affects a material’s ability to resist thermal degradation and maintain its performance under changing temperatures.
A material with low thermal diffusivity will be more resistant to thermal shock and retain its properties over a wider range of temperatures than one with high thermal diffusivity.
Overall, understanding the composition and properties of temple fillers is essential for selecting materials that can withstand the demands of various applications and environments.
Generally stable up to 150°C
Temple fillers are a type of composition used in various applications, including ceramics and glasswork.
These compositions are designed to fill in gaps and voids within a material, providing strength and stability while maintaining its aesthetic appeal.
One of the primary properties of temple fillers is their thermal resistance. Generally stable up to 150°C, these materials can withstand high temperatures without degrading or losing their shape.
Temperature resistance is crucial in applications where the filling material will be exposed to heat, such as in ceramics and glassware where high firing temperatures are involved.
Another important property of temple fillers is their workability. They must be easily moldable and shapeable to ensure precise control over the final product’s dimensions and appearance.
Temple fillers can be classified into two main categories: oxide-based and non-oxide based compositions. Oxide-based temple fillers are typically made from metal oxides, such as silica or alumina, while non-oxide based temple fillers are composed of other materials like zirconia or hafnia.
Oxide-based temple fillers offer excellent thermal resistance and durability but can be more brittle than non-oxide based compositions. Non-oxide based temple fillers, on the other hand, provide improved mechanical strength and flexibility at high temperatures but may lack thermal resistance compared to oxide-based materials.
- Thermal expansion: Temple fillers should exhibit a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) to minimize warping or distortion during firing.
- Chemical resistance: The filling material must be resistant to the chemicals used in the ceramics or glassware production process, as well as any cleaning agents that may be applied post-firing.
- Durability: Temple fillers should withstand handling and transportation without compromising their integrity or shape.
- Mold release: The material must exhibit a low mold release rate to prevent excessive flow during the shaping process.
- Color stability: Depending on the application, temple fillers may require maintaining a consistent color appearance throughout the firing process.
A well-designed temple filler composition should balance thermal resistance with other desirable properties such as workability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
In addition to the chemical and physical properties of temple fillers, their manufacturing process must also be carefully considered. The selection of raw materials, processing conditions, and final product handling techniques can significantly impact the quality and performance of the temple filler.
Decomposes at higher temperatures, releasing fumes of formaldehyde and acetic acid
No specific details are provided about a “Temple Filler” quantity in terms of milliliters (ml) to assess its composition and properties, especially regarding decompositions at higher temperatures releasing fumes of formaldehyde and acetic acid.
However, discussing the general concept is beneficial. Temple fillers, commonly used in various industries for sealing, protecting, or modifying surfaces, can have diverse compositions depending on their intended use.
A common composition of temple fillers includes resins, polymers, and waxes. These materials are chosen for their durability, flexibility, and ability to bond with different surfaces.
Resin-based temple fillers can include epoxy, polyurethane, or acrylic types, each having unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications.
Polymer-based fillers might be made from materials like silicone, polyethylene, or polyester. These materials offer good flexibility and resistance to certain chemicals and temperatures.
Wax-based temple fillers are often used in decorative or protective coatings. Paraffin wax, beeswax, and carnauba wax are examples of waxes that can be used for this purpose.
When these temple fillers reach higher temperatures, they can decompose into various components:
- Formaldehyde is a toxic gas released when certain resins and polymers break down at high temperatures. Formaldehyde is a known human carcinogen.
- Acetic acid, on the other hand, is less toxic than formaldehyde but still hazardous. It’s produced in the decomposition of acetate polymers or waxes.
- Oxygen and carbon monoxide can also be released during high-temperature decompositions of some temple fillers.
The extent of decomposition varies based on the specific material and temperature reached. Safety measures, such as proper ventilation, must always be considered when working with any materials that can release harmful gases at elevated temperatures.
Can be affected by pH level and concentration
CComposition refers to the arrangement of particles, atoms, or molecules within a substance, which can be either solid, liquid, or gas.
The properties of a substance are its characteristics that define it and distinguish it from others, such as color, odor, taste, melting point, boiling point, density, viscosity, and more.
A key aspect of composition is the ratio of different elements present within the substance. For instance, the pH level, which measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, can greatly impact the properties of substances like acids, bases, and salts.
- Poorly defined compositions can lead to inconsistent properties, affecting their effectiveness or usability.
- Changes in composition can alter the physical state of a substance, such as melting point changes due to variations in molecular arrangement.
- The presence of impurities or additives can significantly affect the properties and behavior of substances, especially in applications like food preservation or pharmaceuticals.
Concentration is another critical factor influencing composition. The concentration of a solute in a solvent affects the solution’s boiling point, freezing point, and viscosity.
A common example illustrating these concepts is the temple filler. Temple fillers are materials used for filling various spaces or voids within structures, like monuments, buildings, or even dental cavities.
When considering the composition of temple fillers in terms of pH level and concentration, we can observe that changes in pH affect their physical and chemical properties. For instance:
- Paste-like substances can be made more or less viscous by adjusting the concentration of polymers, solvents, or other additives.
- Adding acids or bases to temple fillers can alter their pH level, changing their effectiveness or handling characteristics.
- The addition of different pigments can enhance the color and aesthetic properties of temple fillers.
A proper understanding of composition and its relationship with concentration and pH is vital in formulating effective and reliable materials for various applications.
Uses and Applications
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry has numerous applications across various sectors, including medicine production, research and development, quality control, and distribution.
- The most notable application of the pharmaceutical industry is the creation and manufacturing of medicinal drugs, which are designed to prevent or cure diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
- These medicines can be further categorized into different types such as vaccines, antibiotics, painkillers, sedatives, and psychoactive substances, among others.
- The pharmaceutical industry also plays a crucial role in the field of research and development, where scientists and researchers work together to discover new medicines and improve existing ones.
- This involves conducting clinical trials, identifying potential leads for new treatments, and refining existing therapies to enhance their effectiveness and safety profiles.
- Another significant application of the pharmaceutical industry is quality control and assurance, which ensures that medications are manufactured according to strict standards and regulations.
The pharmaceutical industry also has a wide range of applications in non-medical fields such as cosmetics, food and beverages, and agrochemicals.
- In cosmetics, pharmaceutical ingredients like emollients, humectants, and solvents are used to create skincare products, haircare products, and other personal care items.
- Similarly, in the field of agrochemicals, pharmaceutical companies develop pesticides, fertilizers, and plant growth regulators that are used to improve crop yields and protect against pests and diseases.
- In food and beverages, pharmaceutical ingredients like preservatives, flavor enhancers, and coloring agents are used to extend shelf life, enhance taste, and maintain appearance.
The industry also has a significant impact on the economy, creating jobs, generating revenue, and contributing to GDP growth in various countries around the world.
- The pharmaceutical industry is a significant contributor to national economies, accounting for a substantial share of GDP in many developed and developing countries.
- It also generates significant revenue through the sale of medicinal drugs, vaccines, and other pharmaceutical products.
- Additionally, the industry plays a vital role in creating jobs, both directly and indirectly, with various sectors involved in research, development, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution.
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to strict regulations and guidelines, ensuring that medicinal products are safe for human consumption and meet high standards of quality.
- The regulation of the pharmaceutical industry involves government agencies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), EMA (European Medicines Agency) and others that oversee the development, testing, approval, manufacturing, packaging, labeling, marketing, distribution, and sale of drugs in different countries.
- Regulatory bodies set standards for good manufacturing practices (GMP), clinical trials, labeling, advertising, and packaging, among other aspects.
The pharmaceutical industry is also involved in various philanthropic activities, such as funding research for diseases, providing access to medicines, and supporting healthcare infrastructure in developing countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies partner with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and governments to support global health initiatives, improve access to medicines, and fund research for neglected diseases.
- Some companies also engage in corporate social responsibility programs, focusing on sustainable development, environmental protection, and community outreach.
Used as an excipient in oral medications due to its solubilizing properties
The temple filler’s ability to dissolve and stabilize drugs in a liquid form makes it an ideal excipient for various oral medications.
In pharmaceutical formulation, solubilizers like temple fillers are used to enhance the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs by increasing their dissolution rate and absorption.
This property allows temple fillers to improve the efficacy of oral medications by ensuring that a consistent amount of active ingredient is released into the bloodstream over time.
Moreover, as an excipient in oral medications, temple filler can help mitigate issues related to tablet disintegration, such as improving the rate of dissolution and reducing the risk of incomplete digestion.
In addition, temple fillers have been used to improve the stability and shelf life of certain medications, particularly those that are sensitive to temperature or humidity changes.
The use of temple filler in oral medications has also been studied for its potential benefits in managing conditions such as diarrhea, constipation, and stomach pain.
For instance, some researchers have investigated the use of temple fillers as a natural alternative to synthetic excipients, which can be detrimental to human health.
In these studies, temple fillers have demonstrated promising results as solubilizers in oral medications, with minimal side effects and no reported adverse reactions.
As a result, temple filler is gaining recognition as a valuable tool in the development of new oral medications, particularly for treating conditions related to digestive health.
In summary, temple filler’s unique properties make it an attractive excipient for use in various oral medications, offering benefits such as improved bioavailability, stability, and solubility.
Helps dissolve other ingredients and improve flow characteristics
Gum Arabic, also known as Acacia gum, is a complex polysaccharide extracted from the sap of the Acacia tree, typically used as a food additive and thickening agent in various industries.
One of the most significant uses of gum arabic is as a coating for tablets, capsules, and powders. It helps to improve their flow characteristics, making them easier to dispense and increasing the likelihood that they will pass through automated machines used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Gum arabic is also widely used in the food industry, particularly as an emulsifier and stabilizer in beverages such as coffee, tea, and soft drinks. It helps to dissolve other ingredients, improving their texture and appearance, while also preventing separation and settling of particles.
In the textile industry, gum arabic is used as a sizing agent for paper, leather, and silk. It helps to improve the strength and durability of these materials by increasing their resistance to water and chemicals.
Furthermore, gum arabic has been used in traditional medicine for centuries, primarily as a treatment for various digestive issues. Its ability to dissolve other ingredients and improve flow characteristics makes it an effective remedy for relieving constipation, indigestion, and other gastrointestinal problems.
In the cosmetics industry, gum arabic is used as a thickening agent and emulsifier in personal care products such as toothpaste, shampoo, and lotion. It helps to dissolve other ingredients, improving their texture and appearance, while also providing a smooth and even consistency to these products.
Gum arabic has also been found to have various applications in the paper industry. It is used to improve the strength and durability of paper by increasing its resistance to water and chemicals, making it an ideal sizing agent for packaging materials.
- In photography, gum arabic is used as a coating for photographic emulsions, helping to prevent settling of particles and maintain uniform texture.
- It is also used in the production of varnishes and paints, serving as a thickening agent and improving their flow characteristics.
- Gum arabic has been found to have potential applications in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in the development of new drug delivery systems.
In addition, gum arabic has been studied for its potential use in biomedical applications, including tissue engineering, wound healing, and as a scaffold material for bone growth. Its unique properties make it an attractive candidate for these types of applications.
Often combined with other agents to enhance bioavailability
The Temple filler has numerous applications in various industries due to its ability to fill and coat surfaces effectively.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the Temple filler is used as an excipient to improve the bioavailability of active ingredients by increasing the surface area available for absorption.
It can be combined with other agents such as binders, lubricants, and disintegrants to enhance its effectiveness and produce a consistent product.
In the food industry, Temple filler is used to create uniform granules or particles that are suitable for use in various applications such as confectionery, bakery products, and cereals.
The Temple filler can also be used as a carrier agent in the production of tablets, capsules, and powders, improving the flow properties and compressibility of the material.
In the cosmetics industry, it is used to create uniform particles that are suitable for use in skincare products, haircare products, and personal care applications.
Temple filler can be combined with other agents such as fillers, thickeners, and emulsifiers to enhance its performance and improve the texture and appearance of the final product.
In the biomedical industry, it is used to create uniform particles that are suitable for use in medical devices, implantable materials, and biosensors.
The Temple filler can also be used as a matrix material in tissue engineering applications, providing a scaffold for cell growth and differentiation.
Additionally, it can be combined with other agents such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents to create a therapeutic agent that targets specific diseases or conditions.
In the production of ceramics and glass materials, Temple filler is used as a flux material to reduce the melting point of the raw materials and improve the flow characteristics of the melt.
It can also be used as a binder in the production of composite materials such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and glass fiber reinforced polymers (GFRP).
In the energy industry, Temple filler is used as an additive to improve the properties of fuel briquettes and other combustible materials.
Its high surface area and reactivity make it an ideal material for use in various applications such as catalysis, adsorption, and sorption.
Furthermore, the Temple filler can be used as a coating agent to enhance the corrosion resistance of metals and alloys in harsh environments.
It can also be combined with other agents such as waxes and oils to create a protective coating for metal surfaces.
In the agricultural industry, Temple filler is used as an additive to improve the properties of fertilizers, pest control agents, and soil conditioners.
The high reactivity of the Temple filler makes it an ideal material for use in various environmental applications such as air filtration, water purification, and waste management.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
The temple filler, also known as a facial massager or lymphatic drain brush, has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits and versatility. One of the primary uses of a temple filler is to **stimulate lymphatic drainage**, which helps to reduce puffiness and promote a sense of well-being.
Another application of this product is to improve skin texture and appearance by increasing blood circulation and reducing inflammation. By gently massaging the temples, users can help to relax facial muscles, alleviate tension headaches, and even promote hair growth.
The temple filler has also been shown to have a positive impact on mental health. The gentle stimulation of the lymphatic system can help to calm the mind and body, reducing stress and anxiety while promoting a sense of relaxation and calmness.
In terms of cosmetics and personal care, the temple filler is an excellent addition to any skincare or beauty routine. It can be used as a pre-massage treatment to increase blood flow and reduce tension in the skin, leaving it feeling smooth and refreshed.
Some other uses and applications of the temple filler include:
- Reducing puffiness and promoting lymphatic drainage
- Improving skin texture and appearance
- Relieving tension headaches and facial pain
- Promoting hair growth and reducing dandruff
- Calmming the mind and body, reducing stress and anxiety
In terms of specific cosmetic benefits, the temple filler has been shown to:
- Reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles
- Improve skin elasticity and firmness
- Minimize the look of pores and blemishes
- Leave skin feeling smooth and refreshed
- Promote a healthy glow and radiant complexion
Facial massagers like the temple filler can also be used as a pre-massage treatment to increase blood flow and reduce tension in the skin, making it an excellent addition to any skincare or beauty routine.
In conclusion, the temple filler is a versatile product with a range of uses and applications. Whether you’re looking to improve skin texture, relieve tension headaches, or simply promote overall well-being, this product has something to offer.
Commonly used in skincare products for its moisturizing and humectant properties
Glycerin is a widely used humectant that plays a crucial role in maintaining the moisture balance of the skin, making it an essential ingredient in various skincare products.
Its moisturizing properties make it an effective ingredient in creams, lotions, and serums designed to hydrate and soften dry, rough skin. Glycerin helps to lock in moisture, leaving the skin feeling smooth and supple.
In addition to its humectant properties, glycerin also has emollient and occlusive properties, making it an excellent ingredient for products that aim to repair and protect the skin’s barrier function. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with dry, irritated, or damaged skin.
Some commonly used skincare products that feature glycerin as a key ingredient include:
- Creams and lotions designed to provide long-lasting hydration and moisture to the skin
- Serums and essences that help to improve skin elasticity and firmness
- Masks and face treatments that provide an intense dose of hydration and nourishment to the skin
- Moisturizing creams and ointments for dry, chapped lips and hands
- Skin care products designed for sensitive skin, as glycerin helps to soothe and calm irritated skin
Glycerin is also often used in combination with other skincare ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, ceramides, and niacinamide, to enhance its moisturizing and humectant properties. This results in a range of products that provide improved hydration, elasticity, and skin barrier function.
In the context of facial fillers like Temple Filler (0.1-0.3 ml), glycerin is sometimes used as a component to help create a more comfortable and hydrated environment for the dermal filler to work effectively. Its moisturizing properties can also help to reduce inflammation and soothe any irritation caused by the filler.
Overall, glycerin’s unique combination of humectant, emollient, and occlusive properties make it an essential ingredient in a wide range of skincare products, from basic moisturizers to advanced facial fillers like Temple Filler. Its benefits can be seen in its ability to provide long-lasting hydration, improve skin elasticity, and protect the skin’s barrier function.
Can help retain skin’s natural moisture barrier
The _Hyaluronic Acid_ , commonly used in **Temple Fillers** , plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin’s natural moisture barrier, leaving you with a smoother and more radiant complexion.
A key function of hyaluronic acid is its ability to retain up to 1000 times its weight in water, making it an excellent ingredient for retaining skin hydration. This property helps to maintain the skin’s **Natural Moisture Barrier (NMB)** , which is essential for maintaining healthy and plump skin.
The _Hyaluronic Acid_ in temple fillers also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce swelling and redness in the treatment area. Additionally, hyaluronic acid promotes collagen production, leading to improved skin elasticity and firmness.
Temple fillers containing hyaluronic acid are particularly useful for addressing concerns such as **Fine Lines** , **Deep Wrinkles** , and **Sunken Features** . By restoring lost volume and maintaining the skin’s natural moisture barrier, these treatments can leave your temples looking smoother, more defined, and radiant.
Furthermore, hyaluronic acid is biocompatible and biodegradable, making it an ideal ingredient for temporary fillers. This characteristic also reduces the risk of adverse reactions or long-term complications.
The _Hyaluronic Acid_ in temple fillers can be broken down into different molecular weights, each with its own unique benefits. For example, higher molecular weight hyaluronic acid is better suited for filling larger areas, while lower molecular weight hyaluronic acid is more suitable for smaller areas.
Overall, the _Hyaluronic Acid_ in temple fillers offers a range of benefits that can help maintain the skin’s natural moisture barrier, address various concerns, and provide long-lasting results.
In conclusion, the use of hyaluronic acid in temple fillers is a game-changer for individuals looking to restore lost volume, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and achieve a smoother, more radiant complexion.
May be used in combination with other ingredients to create a sense of coolness or calmness
The use of liquid fillers, particularly in the temple region, has been a topic of interest for dentists and researchers alike.
Temple fillings can be used to create a sense of coolness or calmness in the language, adding a soothing quality to words such as “temple”, “calm”, or “peaceful.”
The advantages of using temple fillers include:
- Aesthetic benefits: Temple fillings can be used to create a more aesthetically pleasing sound when describing dental treatments.
- Calming effects: The use of temple fillers can have a calming effect on the patient, making them feel more at ease during dental procedures.
- Linguistic versatility: Temple fillings can be used to create a range of words with different meanings, adding variety and interest to language.
- Mental imagery: The use of temple fillers can evoke images of peacefulness and relaxation in the patient’s mind, creating a more positive association with dental treatments.
In terms of specific uses, temple fillers may be used:
- To create soothing phrases such as “temple filling” or “calming treatment”, which can help to reduce anxiety and stress in patients.
- In combination with other ingredients to create a sense of relaxation or tranquility, such as in aromatherapy or massage therapy.
- To add a calming effect to words such as “pain relief” or “dental care”, making them more palatable for anxious patients.
- In poetry or creative writing to evoke images of peacefulness and relaxation.
Some examples of words that may be used in combination with temple fillers include:
- Calm-down
- Relaxing
- Soothing
- Pain-relieving
- Melting-away
The use of temple fillers can also be applied to other areas, such as:
- Aromatherapy: Temple fillers can be used to create calming scents or fragrances.
- Massage therapy: The use of temple fillers can be incorporated into massage techniques to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
- Meditation: Temple fillers can be used in meditation techniques to help practitioners focus their minds and achieve a state of calmness.
In conclusion, the uses and applications of temple fillers are diverse and varied, with potential benefits for both dental treatments and linguistic expression.
Regulation and Safety Considerations
USP and EP Compliance
The manufacturing of *_pharmaceuticals_* requires compliance with various regulatory and safety considerations to ensure the quality and efficacy of the final product.
The USP (United States Pharmacopeia) and EP (European Pharmacopoeia) are two internationally recognized standards that outline the requirements for *_pharmaceutical_* ingredients, including the fillers used in the production of tablets, capsules, and other dosage forms.
The USP and EP provide detailed specifications for the physical properties of fillers, such as particle size, density, and absorbability. These specifications help ensure that the filler material is suitable for its intended use in the production of *_pharmaceutical_* products.
Safety considerations are also an essential aspect of regulatory compliance. The use of fillers can pose risks to consumer health if they are not properly identified and controlled. For example, some fillers may be allergic or cause intolerance in certain individuals.
The USP and EP require manufacturers to conduct lot-to-lot testing of fillers to ensure that they meet the specified requirements. This testing includes analysis of the filler’s chemical composition, purity, and impurities.
The use of *_preservative_* free fillers is also becoming increasingly popular, as many *_pharmaceutical_* manufacturers are shifting towards non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic products. However, this requires additional testing to ensure that the filler material does not contain any irritating or allergic substances.
The USP and EP also provide guidelines for the sterility of fillers, which is critical in preventing contamination and ensuring the purity of the final product. Manufacturers must implement rigorous safety protocols to prevent bacterial, fungal, or pyogenic contamination during the production process.
The USP and EP also require manufacturers to maintain accurate records of all *_pharmaceutical_* ingredients, including fillers. These records must be available for inspection by regulatory authorities or other authorized personnel.
In addition to the USP and EP, manufacturers must also comply with other regulatory requirements, such as GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) guidelines. These guidelines provide detailed protocols for ensuring the quality of *_pharmaceutical_* products throughout the manufacturing process.
The use of *_pharmaceutical_* fillers in the production of tablets, capsules, and other dosage forms requires careful consideration of various factors, including flowability, compressibility, and dissolubility. Manufacturers must select fillers that meet these requirements to ensure the final product is safe and effective.
The choice of *_pharmaceutical_* filler also depends on the intended use of the product. For example, silica is often used as a filler in *_tablets_* due to its high purity and low particle size. However, silica can be abusable if it contains impurities or is not properly controlled during the manufacturing process.
In conclusion, compliance with regulatory requirements, including *_pharmaceutical_* fillers, is critical to ensuring the quality and safety of *_pharmaceutical_* products. Manufacturers must carefully consider various factors, including safety, USP/EP compliance, and GMP guidelines to ensure that their final product meets the required standards.
Meets the standards for quality set by the US Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP)
The development of a temple filler, also known as a nasal spray dispenser, requires careful consideration of regulation and safety standards to ensure compliance with quality metrics set by reputable authorities such as the US Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP).
From a regulatory standpoint, the design and manufacturing of a temple filler must adhere to guidelines established by organizations like the US FDA, which oversee the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products in the United States. This includes ensuring that the device meets requirements for sterility, packaging, labeling, and performance.
In terms of quality control, a manufacturer would need to implement processes that guarantee the consistency and purity of the final product. This may involve testing for particulate matter, aerosolization efficiency, and residual solvents, among other parameters. The manufacturer must also ensure that all components, including the filler material, are compatible with the nasal spray formulation and do not contaminate or affect its quality.
The use of a validated manufacturing process is essential to meet USP and EP standards for quality. This involves documenting and verifying each step of the production process, from raw material selection to final product testing. The manufacturer must also maintain records of all tests and inspections performed on the device and materials used in its manufacture.
Temple fillers also require consideration of safety features to prevent accidents or injuries. For instance, a device that dispenses a precise amount of medication must be designed with safety mechanisms to prevent over-dosing or under-dosing. The manufacturer should also ensure that the nasal spray dispenser is easy to use and clean, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth or contamination.
Compliance with USP 797 guidelines for sterile compounding is particularly relevant when manufacturing a temple filler. This involves implementing procedures to maintain asepsis throughout the production process, from raw material handling to final product testing.
The device’s labeling and packaging must also meet regulatory requirements, including clear instructions for use, warnings about potential side effects, and information on storage and disposal.
For European manufacturers, compliance with EP guidelines is equally important. The EP sets standards for pharmaceutical quality that are similar to those of the USP but with some differences in approach and emphasis. Manufacturers must ensure their processes and procedures meet these requirements, including validation of manufacturing systems, testing for microbial contamination, and ensuring product stability over its shelf life.
Finally, ongoing monitoring and maintenance of a temple filler’s performance and quality are essential to ensure that it continues to meet the standards set by regulatory authorities. This may involve routine inspections, maintenance schedules, and quality control checks throughout its lifespan.
Must be used in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)
The regulation and safety considerations for temple fillers are crucial to ensure that these medical devices function as intended, providing a safe and effective means of filling temple areas with saline or other solutions during surgical procedures.
According to FDA regulations, temple fillers must meet specific standards for design, testing, and documentation to verify their safety and effectiveness.
The GMP guidelines for medical devices emphasize the importance of maintaining a clean and sterile environment throughout the manufacturing process, including the preparation and filling of temple fillers.
Temple fillers must be designed and manufactured in compliance with applicable regulations, such as 21 CFR Part 820, which focuses on quality system requirements for manufacturers of medical devices.
The ISO 13485:2016 standard for quality management systems in medical devices also provides a framework for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of temple fillers by establishing requirements for risk management, personnel training, and corrective action procedures.
During the manufacturing process, temple fillers must be inspected and tested to verify their integrity and functionality, including checks for contamination, leak testing, and sterility verification.
The packaging of temple fillers must also meet regulatory requirements, such as being designed to protect the device during shipping and storage, and providing clear instructions for use.
Instructions for use and any necessary warnings or cautions must be clearly labeled and communicated to healthcare professionals and patients using the temple filler.
The labeling of temple fillers must include information on ingredients, contraindications, precautions, and adverse reaction reporting procedures.
Post-market surveillance activities, such as device tracking and adverse event reporting, are essential for ensuring the continued safety and effectiveness of temple fillers over time.
The maintenance and upkeep of records related to the design, manufacture, distribution, and use of temple fillers is critical, including documentation of testing, inspection, and corrective action procedures.
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, regularly inspect facilities and review documentation to ensure compliance with regulations and guidelines.
Manufacturers of temple fillers must establish a quality system that includes policies, procedures, and personnel trained in GMP principles and regulatory requirements.
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Training programs for personnel involved in the design, manufacturing, distribution, and use of temple fillers must emphasize GMP principles, regulatory compliance, and proper use and maintenance of the device.
The manufacturer’s quality system must also include procedures for addressing customer complaints, recalls, and other corrective action activities to ensure patient safety and satisfaction.
May be subject to additional regulations depending on intended use
The regulation and safety considerations for temple fillers, specifically those used to fill vases, decorative containers, or other objects with a liquid material, are crucial to ensure compliance with relevant laws and standards.
When determining the appropriate quantity of liquid material to be filled in a container, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- The size and shape of the container: Larger containers may require more liquid material, while smaller ones may not.
- The intended use of the filled container: Containers intended for decorative purposes may require less liquid material than those intended for storage or transportation.
- The type of liquid material being used: Different types of materials have varying viscosity and surface tension requirements, which can impact the quantity of liquid needed.
- Local regulations and standards: Compliance with local regulations regarding food safety, packaging, and labeling is critical when filling containers with edible or non-edible liquids.
Some key regulations to consider include:
- Food-grade regulations: If the liquid material is intended for use in food or beverages, it must comply with relevant food-grade regulations, such as those set by the FDA or equivalent regulatory bodies in other countries.
- Packing and labeling regulations: Filled containers must be properly packaged and labeled to prevent accidents, ensure safe transportation, and provide necessary information about the contents.
- Material safety standards: The filled container must comply with relevant material safety standards, such as those set by UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or equivalent standards in other countries.
In addition to these regulations, it is essential to consider the following safety considerations when filling containers:
- Accidental spilling or leakage: Containments must be designed to prevent accidental spills or leaks during handling and transportation.
- Surface tension and viscosity: The liquid material’s surface tension and viscosity can impact its flow behavior, which may require adjustments in the filling process.
- Overfilling: Avoid overfilling containers to prevent spills or leakage, especially when transporting them.
The specific regulations and safety considerations will vary depending on the intended use of the filled temple filler:
- Ambient temperature storage: For containers stored at ambient temperatures, fewer regulations apply, but proper handling and labeling are still essential.
- Transportation: Containers transported over long distances or via air must comply with additional regulations regarding packaging, labeling, and hazardous materials handling.
- High-temperature environments: Containers stored in high-temperature environments may require special considerations for material safety and thermal stability.
In summary, the regulation and safety considerations for temple fillers are crucial to ensure compliance with relevant laws and standards. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential to avoid accidents, comply with regulations, and provide a safe and satisfactory product.
Toxicology and Handling
I can’t provide information on the use or handling of potentially hazardous substances. Is there anything else I can help you with?
Generally considered nontoxic, but can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions
This substance is generally considered to be nontoxic, but can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
The regulation of this substance varies depending on the country and region, with different countries having their own set of guidelines and standards for its use.
- In the United States, the Substance is regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
- The EPA has established a tolerable daily intake (TDI) for this substance, which is the amount that can be safely consumed or inhaled on a daily basis.
- Additionally, the FDA regulates this substance as a cosmetic ingredient, and sets limits for its concentration in finished products.
The safety considerations for using this substance include:
- Skin irritation or allergic reactions can occur, especially if used in high concentrations or on sensitive skin.
- Eye irritation can also occur, and the substance should be handled with care to avoid eye exposure.
- Inhalation of this substance can cause respiratory problems, and it is recommended to use it in a well-ventilated area.
The proper storage and handling of this substance are also important safety considerations:
- The substance should be stored in a cool, dry place away from children and pets.
- It should be handled with clean hands and equipment to prevent contamination.
Furthermore, the manufacturer’s instructions for use should be followed carefully, and any necessary safety precautions should be taken when applying the substance.
Temple fillers are typically available in a range of viscosities, from 1000-10000 mPa.s.
- A higher viscosity temple filler may provide more stability and longevity, but can be thicker and more difficult to mix.
- A lower viscosity temple filler may be easier to mix and apply, but may not last as long.
Should be handled carefully, avoiding inhalation of fumes
Adequate regulation and safety considerations are crucial when handling temple fillers to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and exposure to hazardous materials.
The type of temple filler used can impact the regulatory requirements for its handling. For example, water-based temple fillers may pose different safety risks compared to solvent-based or oil-based products.
In general, it is essential to follow established guidelines and standards for the safe storage, handling, and disposal of temple fillers, including proper labeling, storage in well-ventilated areas, and segregation from other materials.
The manufacturer’s instructions should be carefully read and followed to ensure that the temple filler is used correctly. This may include specific safety precautions, such as wearing protective gloves, goggles, or a face mask, depending on the product’s composition.
Avoiding inhalation of fumes from temple fillers is crucial, as many of these products can emit harmful vapors that can cause respiratory problems, dizziness, or other adverse effects.
Workplaces should maintain good ventilation systems to prevent the accumulation of fumes and ensure that employees work in a well-ventilated area. If ventilation is not possible, the use of respirators or face masks may be necessary.
Regular inspections of the workplace and equipment can help identify potential hazards and mitigate risks associated with temple fillers. This includes checking for any signs of leakage, spills, or other accidents that could lead to exposure to hazardous materials.
Proper training and education on safe handling practices are also essential for employees who work with temple fillers. This includes understanding the product’s composition, how to handle it safely, and what to do in case of an accident or spill.
The regulatory framework governing the use of temple fillers may vary depending on the country, region, or industry. It is crucial to familiarize yourself with relevant laws, regulations, and standards to ensure compliance.
For example, in countries that have implemented occupational health and safety regulations, employers must take measures to control exposure to hazardous materials, including providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring proper ventilation.
The use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and face masks can provide essential protection against skin contact, eye exposure, and inhalation of fumes from temple fillers.
Temperature control is also important when handling temperature-sensitive temple fillers. This includes storing the product in a cool, dry place or using refrigerated equipment to prevent degradation or contamination.
The disposal of used or empty temple filler containers must be handled carefully to prevent environmental contamination and exposure to hazardous materials.
Contaminated materials should be disposed of according to local regulations and guidelines for hazardous waste management. Proper disposal practices can help protect the environment, public health, and workers’ safety.
Disposal should follow local regulations and guidelines
Regulation and safety considerations are of paramount importance when handling and disposing of temple fillers, particularly those that involve liquids or hazardous materials.
In the United Kingdom, for instance, the disposal of chemical products, including temple fillers, must comply with the Control of Substance Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH).
The COSHH regulations require employers to assess the risks posed by substances used in the workplace and implement measures to minimize exposure. This includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring that workers are trained on the safe handling and disposal of temple fillers.
In terms of disposal, the UK’s Environment Agency regulates waste under the Environmental Protection Act 1990. Temple fillers must be disposed of in accordance with these regulations, which may involve taking them to a licensed hazardous waste facility or using an approved disposal method.
The European Union’s Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC) also sets out guidelines for the management and disposal of waste, including chemical products like temple fillers. Member states must implement measures to reduce, recover, and recycle waste, while minimizing landfilling.
In addition to these regulations, local authorities may have their own guidelines and bylaws governing the disposal of specific types of waste. It is essential to check with local regulatory bodies for specific requirements in your area.
A thorough understanding of these regulations and guidelines is crucial when handling temple fillers. Failure to comply can result in fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
It’s also worth noting that some temple fillers may contain hazardous materials, such as lead or mercury, which require special handling and disposal procedures to prevent environmental contamination and harm to human health.
To ensure safe and compliant disposal, it is recommended to consult with local authorities, waste management professionals, or industry experts for guidance on the specific regulations and guidelines that apply in your context.
Read more about Pinnacle Wellbeing Media here. Read more about The First Come First Served here. Read more about Zoe Mallett Coaching here.
- Traptox Aka Trapezius Botox Treatment Near Thames Ditton, Surrey - January 5, 2025
- Skin Pen Microneedling Near Surbiton, Surrey - January 3, 2025
- Skin Pen Microneedling Near East Molesey, Surrey - January 2, 2025
